So, what is the hreflang tag, and why does Google like it?
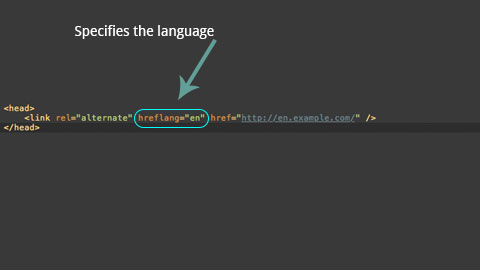
To ensure the right language appears on the page when viewed in various countries, Google introduced (Dec. 2011) and started using the <hreflang> tag. It is code that needs to reside in the <head> tag (or the sitemap.xml file) of your website. This tag specifies the language (ex. US English is "en-us") and allows the search engines to serve up the content you intend depending on the location of the visitor. More specifically in terms of SEO, it gets down to targeting internationally and regionally. You ARE in control of which documents/pages are viewed.
For example, the code looks like this:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="http://en.example.com/" />or like this:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="http://example.com/en/" />The only difference in the 2 links above are the locations of the files in English. You’ll notice the url (href=" ") displays the path where the files are located. Each “/” is a new folder. The first link example above displays the URL in English as a subdomain. "en.example.com/". For more information about subdomains, look here.
The code above is HTML. For me, it’s easy to understand because I am a web developer. I also love explaining it in “English” (no pun intended, lol). So, let’s dive in a little bit deeper and take a look at the code to see what’s going on.
First, let’s start with the beginning.
You will notice, the code starts with <link> tag. This is an HTML tag, that tells the browser there is a connection (link) from this document to an external resource. And looks like this:

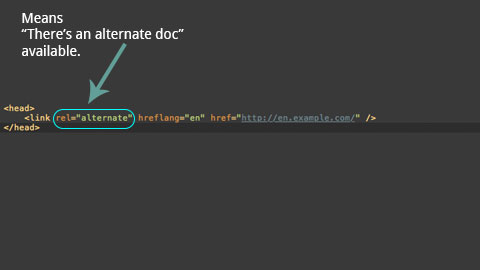
The rel="alternate" part of the link tells the browser that there is an alternate version available, and specifies the relationship between the linked documents.
*Note, the rel=" " tag also accepts other values (here the value is “alternate”) and is a required attribute for the <link> tag.
Here’s a list of values for the rel=" " tag.
You’ll also notice the markup has a pattern…the tag (rel), then an =" ". What you put in the ” ” is the attribute. The syntax is the same pattern.

The <link> tag also supports global attributes in HTML, as well as event attributes in HTML.
Resources::
https://www.google.com/support/webmasters/answer/6059209
https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/189077
http://www.w3schools.com/tags/att_link_rel.asp
http://www.w3schools.com/tags/tag_a.asp
https://moz.com/learn/seo/hreflang-tag
